训练完成模型之后,可以对图片进行预测,还可以实现模型结果可视化,查看分割效果。
运行命令如下:
python predict.py \--config configs/quick_start/bisenet_optic_disc_512x512_1k.yml \--model_path output/iter_1000/model.pdparams \--image_path data/optic_disc_seg/JPEGImages/H0003.jpg \--save_dir output/result
首先解释一下上面命令的参数含义,
–config指定配置文件,其中包含了模型的名称。
–model_path指定模型路径
–image_path指定输入预测的图片路径
–save_dir指定了输出预测结果保存的路径。
还可以通过以下命令进行多尺度翻转预测。
–aug_pred是否开启增强预测
–scales缩放系数,默认为1.0
–flip_horizontal是否开启水平翻转
–flip_vertical是否开启垂直翻转
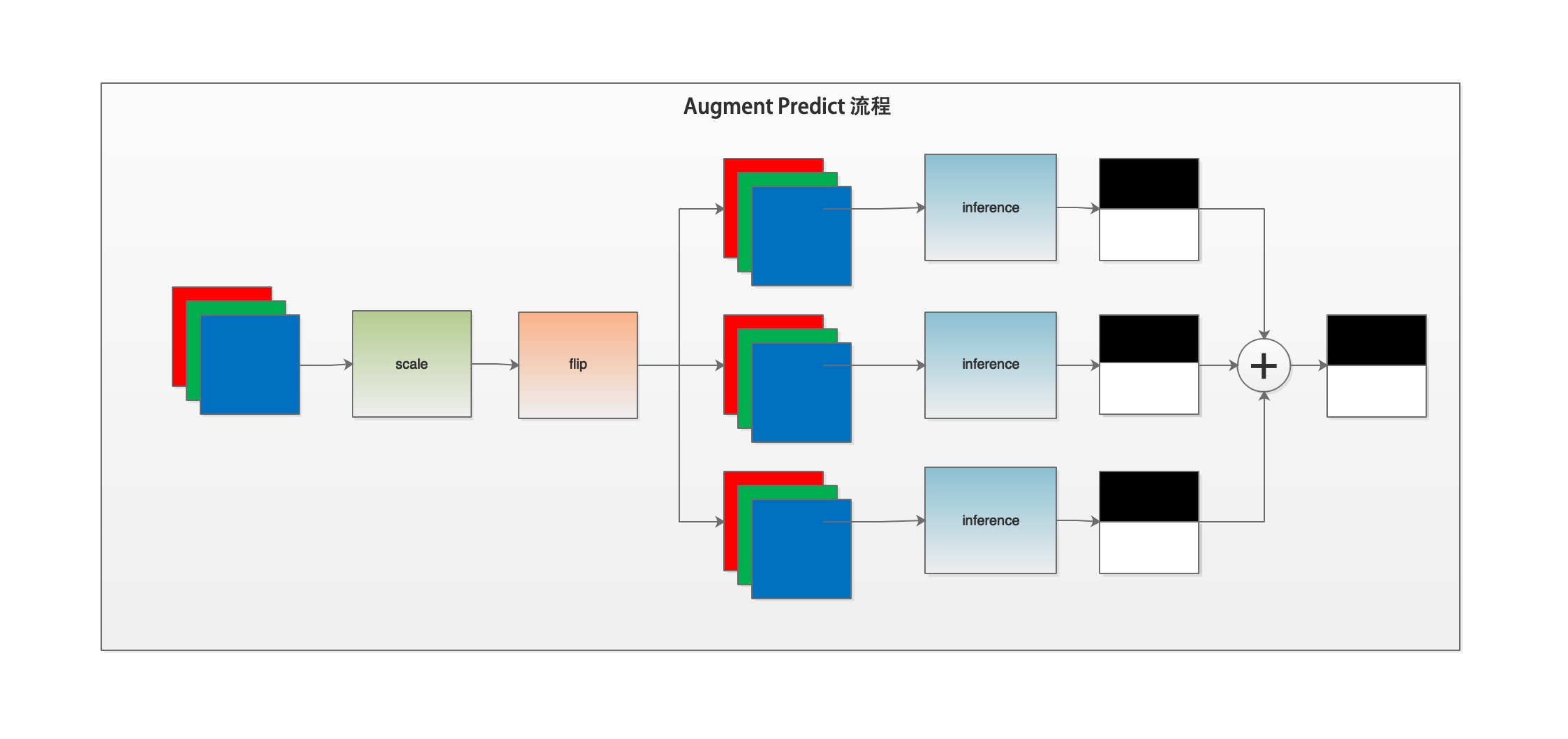
多尺度翻转预测是在普通预测的基础上,对输入图片进行多尺度缩放、水平垂直方向翻转等操作,得出多个预测结果,然后将多个预测结果相加作为最后的输出结果。可以通过下图了解一下预测程序的工作流程。
下面我们解读一下predict.py的代码。
if __name__ == '__main__':#解析传入参数args = parse_args()#执行主体函数main(args)
我们通过解读parse_args函数来了解一下predict.py脚本支持的输入参数与val.py基本一致。
def parse_args():parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Model prediction')# params of prediction# 配置文件路径parser.add_argument("--config", dest="cfg", help="The config file.", default=None, type=str)# 训练好的模型权重路径parser.add_argument('--model_path',dest='model_path',help='The path of model for prediction',type=str,default=None)# 输入的预测图片路径parser.add_argument('--image_path',dest='image_path',help='The path of image, it can be a file or a directory including images',type=str,default=None)#输出的保存预测结果路径parser.add_argument('--save_dir',dest='save_dir',help='The directory for saving the predicted results',type=str,default='./output/result')# augment for prediction#是否使用多尺度和翻转增强的方式预测。这种方法会带来精度的提升,推荐使用parser.add_argument('--aug_pred',dest='aug_pred',help='Whether to use mulit-scales and flip augment for prediction',action='store_true')# 指定缩放系数,1.0为保持尺寸不变,可以指定多个系数,用空格隔开。parser.add_argument('--scales',dest='scales',nargs='+',help='Scales for augment',type=float,default=1.0)# 开启图片水平翻转parser.add_argument('--flip_horizontal',dest='flip_horizontal',help='Whether to use flip horizontally augment',action='store_true')#开启图片垂直翻转parser.add_argument('--flip_vertical',dest='flip_vertical',help='Whether to use flip vertically augment',action='store_true')# sliding window prediction#滑动窗口参数配置,是否开启滑动窗口parser.add_argument('--is_slide',dest='is_slide',help='Whether to prediction by sliding window',action='store_true')# 滑动窗口尺寸parser.add_argument('--crop_size',dest='crop_size',nargs=2,help='The crop size of sliding window, the first is width and the second is height.',type=int,default=None)# 滑动窗口移动的步长,需要指定水平方向和垂直方向两个参数。parser.add_argument('--stride',dest='stride',nargs=2,help='The stride of sliding window, the first is width and the second is height.',type=int,default=None)return parser.parse_args()
以上是输入参数的解析。在main函数中,主要使用core/predict.py模块中的predict函数对图片进行预测。
首先看一下predict函数的代码概要。

然后对predict函数进行代码解读。
def predict(model,model_path,transforms,image_list,image_dir=None,save_dir='output',aug_pred=False,scales=1.0,flip_horizontal=True,flip_vertical=False,is_slide=False,stride=None,crop_size=None):#加载模型权重para_state_dict = paddle.load(model_path)model.set_dict(para_state_dict)#设置模型为评估模式model.eval()added_saved_dir = os.path.join(save_dir, 'added_prediction')pred_saved_dir = os.path.join(save_dir, 'pseudo_color_prediction')logger.info("Start to predict...")#设置进度条progbar_pred = progbar.Progbar(target=len(image_list), verbose=1)#遍历图片列表for i, im_path in enumerate(image_list):#读取图像im = cv2.imread(im_path)#获取图像宽高ori_shape = im.shape[:2]#对图像进行转换im, _ = transforms(im)#新增一个维度im = im[np.newaxis, ...]#将ndarray数据转换为张量im = paddle.to_tensor(im)#是否开启多尺度翻转预测if aug_pred:#开启多尺度翻转预测,则对图片进行多尺度翻转预测pred = infer.aug_inference(model,im,ori_shape=ori_shape,transforms=transforms.transforms,scales=scales,flip_horizontal=flip_horizontal,flip_vertical=flip_vertical,is_slide=is_slide,stride=stride,crop_size=crop_size)else:#如果没有开启多尺度翻转预测,则对图片进行常规的推理预测操作。pred = infer.inference(model,im,ori_shape=ori_shape,transforms=transforms.transforms,is_slide=is_slide,stride=stride,crop_size=crop_size)#将返回数据去除多余的通道,并转为uint8类型,方便保存为图片pred = paddle.squeeze(pred)pred = pred.numpy().astype('uint8')#获取保存图片的名称# get the saved nameif image_dir is not None:im_file = im_path.replace(image_dir, '')else:im_file = os.path.basename(im_path)if im_file[0] == '/':im_file = im_file[1:]#保存结果added_image = utils.visualize.visualize(im_path, pred, weight=0.6)added_image_path = os.path.join(added_saved_dir, im_file)mkdir(added_image_path)cv2.imwrite(added_image_path, added_image)# 保存伪色彩预测结果# save pseudo color predictionpred_mask = utils.visualize.get_pseudo_color_map(pred)pred_saved_path = os.path.join(pred_saved_dir,im_file.rsplit(".")[0] + ".png")mkdir(pred_saved_path)pred_mask.save(pred_saved_path)# pred_im = utils.visualize(im_path, pred, weight=0.0)# pred_saved_path = os.path.join(pred_saved_dir, im_file)# mkdir(pred_saved_path)# cv2.imwrite(pred_saved_path, pred_im)#进度条进度加1progbar_pred.update(i + 1)
在上述代码中,根据输入参数不同,则调用不同的推理函数,已经在上一节评估代码解读中已经介绍,这里不再重复。
以上就是PaddleSeg当前版本主要代码的全部解读。
本系列文章也会定期与PaddleSeg版本更新保持同步。因本人水平有限,若有错误之处还请谅解。
PaddleSeg仓库地址:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleSeg
